#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
struct node { //노드
int key;
node* left = nullptr;
node* right = nullptr;
};
int height(node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int max_h = (height(root->right) > height(root->left)) ? height(root->right) : height(root->left);
return 1 + max_h;
}
node* getNode()
{
node* newnode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
return newnode;
}
node* insertBST(node* root, int newKey)
{
node* p = root;
node* q = nullptr; //부모 노드
//(1) 삽입 위치(q) 탐색
while (p != nullptr)
{
q = p;
if (newKey == p->key)
{
cout << "i " << newKey << " : The key already exists" << endl;
return root;
}
else if (newKey < p->key)
p = p->left;
else
p = p->right;
}
//(2) 새로운 노드 할당
node* newnode = getNode();
newnode->key = newKey;
newnode->right = newnode->left = nullptr;
//(3) q의 자식 노드로 newkey 삽입
if (q != nullptr) //루트노드가 null인 경우
{
if (newKey < q->key)
q->left = newnode;
else
q->right = newnode;
}
if (root == nullptr) return newnode;
return root;
}
int noNodes(node* root, int* num)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
else if (root->right != nullptr)
{
(*num)++;
noNodes(root->right, num);
}
else if (root->left != nullptr)
{
(*num)++;
noNodes(root->left, num);
}
else
(*num)++;
return *num;
}
node* maxNode(node* root)
{
node* p = root;
while (p->right != nullptr)
p = p->right;
return p;
}
node* minNode(node* root)
{
node* p = root;
while (p->left != nullptr)
p = p->left;
return p;
}
node* deleteBST(node* root, int deleteKey)
{//삭제 알고리즘 ;; (1) 삭제할 데이터 위치 탐색 (2) 데이터 이동 (3) 이동한 데이터의 node 삭제
node* p = root; //삭제할 노드
node* q = nullptr; //p의 부모 노드
//(1)삭제 위치 p 탐색
while ((p != nullptr) && (p->key != deleteKey))
{
q = p;
if (deleteKey < p->key)
p = p->left;
else
p = p->right;
}
//노드가 존재하지 않는 경우
if (p == nullptr)
{
cout << "d " << deleteKey << " : The key does not exist" << endl;
return root;
}
//차수가 0인 경우의 삭제 ;; (1) p=root (2) p!=root
if (p->left == nullptr && p->right == nullptr)
{
if (q == nullptr)
root = nullptr;
else {
if (q->left == p) q->left = nullptr;
else q->right = nullptr;
}
delete(p); //p 삭제
}
//차수가 1인 경우의 삭제 ;; (1) p=root (2) p!=root
else if (p->left == nullptr || p->right == nullptr)
{
//현재 갖고 있는 자식 노드를 저장
node* child = (p->left != NULL) ? p->left : p->right;
if (q == nullptr)
root = child;
else
{
if (q->left == p)
q->left = child;
else
q->right = child;
}
delete(p); //p 삭제
}
//차수가 2인 경우의 삭제 ;;
else
{
char flag; //flag 변수 (삭제할 데이터의 위치 탐색)
node* n = root;
if (height(p->left) > height(p->right))
{
n = maxNode(p->left);
flag = 'L';
}
else if (height(p->left) < height(p->right))
{
n = minNode(p->right);
flag = 'R';
}
else
{//양쪽 서브트리의 높이가 동일한 경우 --> 트리의 노드 개수 비교
int Lnode = 0, Rnode = 0;
if (noNodes(p->left, &Lnode) >= noNodes(p->right, &Rnode))
{
n = maxNode(p->left);
flag = 'L';
}
else
{
n = minNode(p->right);
flag = 'R';
}
}
p->key = n->key; //데이터 이동
if (flag == 'L')
p->left = deleteBST(p->left, n->key);
else
p->right = deleteBST(p->right, n->key);
}
return root;
}
void inorderBST(node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
inorderBST(root->left);
cout << root->key << " ";
inorderBST(root->right);
}
int main()
{
ifstream file;
file.open("BST-input.txt");
char mode;
int key;
node* p = nullptr;
node* root = p;
while (!file.eof())
{
file >> mode >> key;
if (mode != 0)
{
if (mode == 'i')
{
p = insertBST(p, key);
inorderBST(p);
cout << endl;
}
else
{
p = deleteBST(p, key);
inorderBST(p);
cout << endl;
}
mode = 0;
}
}
return 0;
}'Programming Language > C, Algorithms' 카테고리의 다른 글
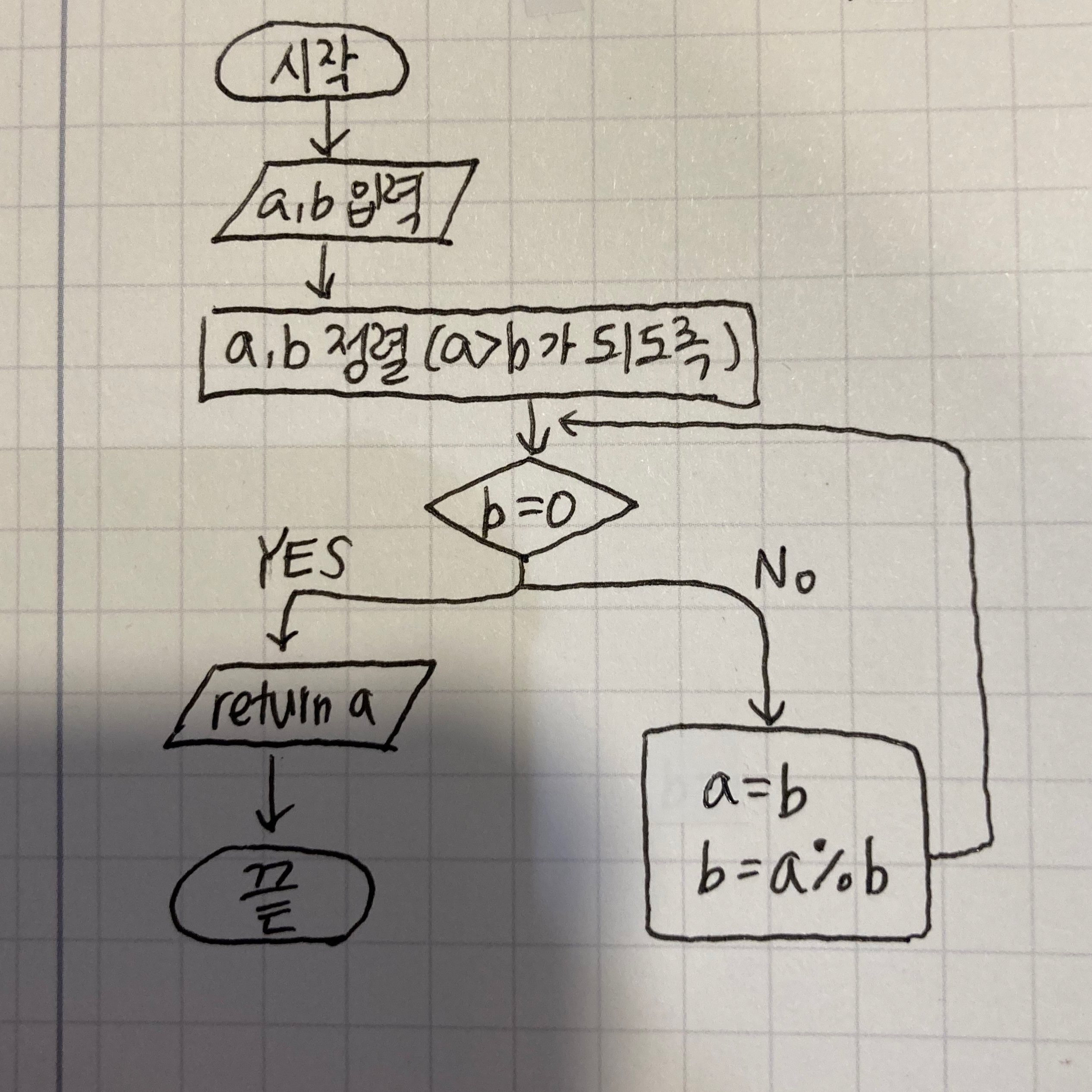
| [C++] 유클리드 호제법 이용, 최대공약수 최소공배수 구하기 (0) | 2022.04.17 |
|---|---|
| [C++] 윤년 계산 및 윤년 목록 출력 (0) | 2022.04.17 |
| [C/C++] 선형방정식의 정수해 구하기 (1) (0) | 2020.04.24 |
| [C/C++] 에라토스테네스의 체를 이용한 소수 출력 (1) (0) | 2020.04.22 |